Our Products
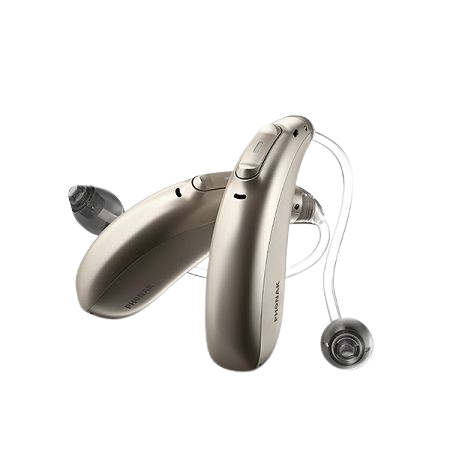

Behind-the-Ear (BTE) Hearing Aids
The Behind-the-ear hearing aids are different from In-ear hearing aids. These BTE hearing devices sit behind your ear and are attached with a thin tube or wire, which is also connected to the earpiece in the ear canal (see the image on the left side for more clarity). This hearing device features a volume control and directional microphone.
Standard BTE:- The hearing device and earpiece are separate components connected by tubing or a thin wire.
- Mini BTE:-Smaller and more sensible than standard BTE models, with a thin tube or wire delivering sound to the ear.
- Receiver-in-Canal (RIC) or Receiver-in-Ear (RIE) BTE:- The receiver is placed inside the ear canal and connected to the main body of the hearing aid behind the ear.
- These Behind-the-ear hearing devices are easy to wear and sit comfortably behind your ear.
- These are the most common hearing aids for mild to severe hearing loss.
- These are simple to use, easy to handle, and come with adjustable settings.
- It comes with cool features like noise reduction and Bluetooth connectivity.
- Packed with Tech, these can have cool features like noise reduction and Bluetooth.
- These are comfy and won’t block your ear canal.
- Behind-the-ear hearing devices amplify sound well, even in noisy places.
- These are tough, water-resistant, built to last, and perfect for active lifestyles.
- These are suitable for everyone: kids, adults, and seniors alike.
- These devices have long-lasting power and options for rechargeable batteries, lasting all day.
Standard BTE:-
The hearing device and earpiece are separate components connected by tubing or a thin wire.- Mini BTE:-Smaller and more sensible than standard BTE models, with a thin tube or wire delivering sound to the ear.
- Receiver-in-Canal (RIC) or Receiver-in-Ear (RIE) BTE:- The receiver is placed inside the ear canal and connected to the main body of the hearing aid behind the ear.
- These Behind-the-ear hearing devices are easy to wear and sit comfortably behind your ear.
- These are the most common hearing aids for mild to severe hearing loss.
- These are simple to use, easy to handle, and come with adjustable settings.
- It comes with cool features like noise reduction and Bluetooth connectivity.
- Packed with Tech, these can have cool features like noise reduction and Bluetooth.
- These are comfy and won’t block your ear canal.
- These are comfy and won’t block your ear canal.
- These are tough, water-resistant, built to last, and perfect for active lifestyles.
- These are suitable for everyone: kids, adults, and seniors alike.
- These devices have long-lasting power and options for rechargeable batteries, lasting all day.
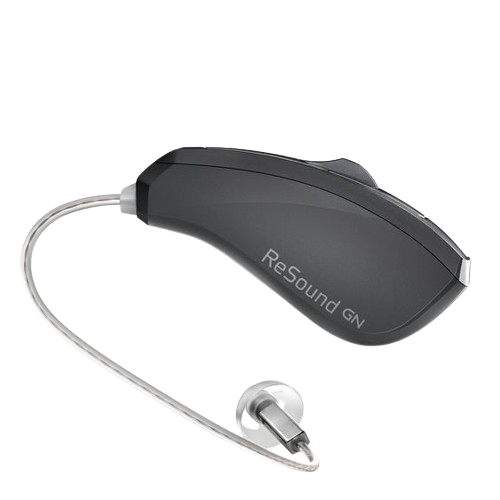




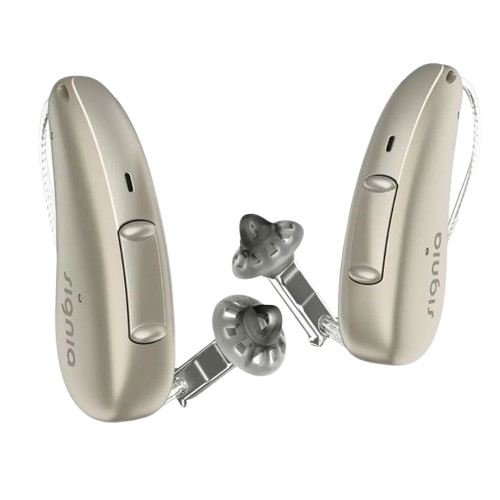

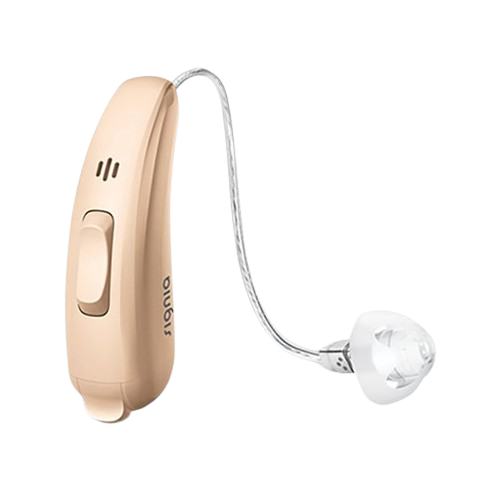
How Do Behind-the-Ear (BTE) Hearing Aids Work?
Behind-the-Ear (BTE) hearing aids are designed to amplify sound and improve hearing for individuals with hearing loss. Here’s a detailed look at how they work:
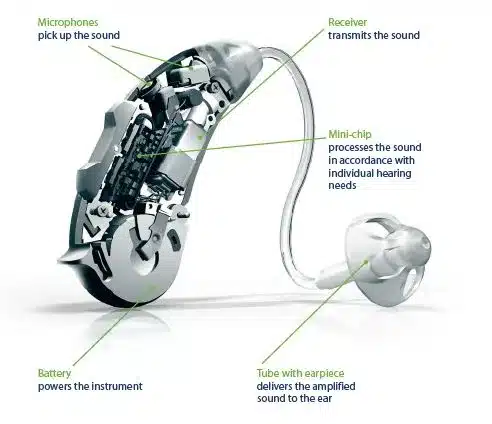
1. Sound Collection:
Microphone
The process begins with one or more microphones located on the part of the hearing aid that sits behind the ear. These microphones pick up sound waves from the environment.
Some BTE hearing aids have directional microphones, which can focus on sounds coming from specific directions, helping to enhance speech in noisy environments.
2. Sound Conversion:
Analog-to-Digital Conversion
The captured sound waves are converted into electrical signals. In modern digital hearing aids, these signals are then converted into digital data by an analog-to-digital converter.
Digital processing allows for sophisticated sound manipulation and customization based on the user’s hearing loss profile.
3. Sound Processing:
Amplifier
The digital signals are processed by the hearing aid’s microprocessor. This processing can include noise reduction, feedback cancellation, and speech enhancement to improve clarity and comfort.
The processed signals are then amplified according to the specific hearing loss needs of the user. The amplification levels are customized during the fitting process by an audiologist.
4. Sound Output:
Receiver (Speaker)
The amplified digital signals are converted back into sound waves by the receiver, which is also called the speaker.
In traditional BTE models, the receiver is located in the hearing aid case behind the ear. In Receiver-in-the-Ear (RITE) or Receiver-in-Canal (RIC) models, the receiver is placed directly in the ear canal for a more natural sound experience.
5. Sound Delivery:
Earmold or Dome
The sound waves are directed through a thin tube or wire to an earmold or dome that fits snugly inside the ear canal.
The earmold or dome helps to deliver the sound efficiently and comfortably into the ear while minimizing feedback.
6. Power Supply:
Battery
BTE hearing aids are powered by batteries. These can be disposable zinc-air batteries or rechargeable lithium-ion batteries.
Rechargeable options are convenient and environmentally friendly, allowing for easy daily recharging.
Additional Features and Technologies:
1. Wireless Connectivity:
Many BTE hearing aids offer Bluetooth connectivity, allowing them to pair with smartphones, TVs, and other devices for direct audio streaming. This enhances the listening experience for phone calls, music, and other media.
2. Telecoil (T-coil):
Telecoil technology allows hearing aids to connect to loop systems in public places, such as theaters and churches, providing a clearer audio signal directly to the hearing aid.
3. Feedback Cancellation:
Modern BTE hearing aids have advanced feedback cancellation algorithms that prevent the annoying whistling sounds that can occur with hearing aids.
4. Noise Reduction:
Digital noise reduction features help to filter out background noise, making it easier to focus on conversations and important sounds.
5. Directional Microphones:
Directional microphones can be programmed to focus on sounds coming from specific directions, improving the ability to hear in noisy environments.
different Types Of BTE Hearing Aids
Behind-the-Ear (BTE) hearing aids come in various types, each designed to meet different needs and preferences. Here’s an overview of the main types of BTE hearing aids:
1. Standard BTE Hearing Aids
Description:
These are the traditional BTE hearing aids with a larger case that rests behind the ear and is connected to a custom earmold via a clear tube.
Suitability:
Suitable for mild to profound hearing loss.
Features:
Often have larger batteries for longer battery life.
More room for additional features and controls.
Advantages:
Robust and durable.
Easy to handle and adjust.
Disadvantages:
Larger size may be more visible.

2. Mini BTE (on-the-ear) Hearing Aids

Description:
A smaller version of standard BTE hearing aids, with a more discreet design.
Often used with thin tubes and open-fit domes that do not completely block the ear canal.
Suitability:
Suitable for mild to moderate hearing loss.
Features:
More aesthetically pleasing due to smaller size.
Allows natural sound to enter the ear canal along with amplified sound.
Advantages:
Less visible and more cosmetically appealing.
Comfortable for many users due to the open-fit design.
Disadvantages:
May not provide enough amplification for severe hearing loss.
3. Receiver-in-the-Ear (RITE) or Receiver-in-Canal (RIC) Hearing Aids
Description:
The receiver (speaker) is placed inside the ear canal, while the rest of the components are housed in a small case behind the ear.
Connected by a thin wire instead of a tube.
Suitability:
Suitable for mild to severe hearing loss.
Features:
Often have advanced features such as Bluetooth connectivity and rechargeable batteries.
Smaller and more discreet than standard BTE models.
Advantages:
Provides a more natural sound experience due to the placement of the receiver.
Less prone to feedback.
Disadvantages:
The receiver in the ear canal can be more susceptible to earwax and moisture.

4. Power BTE Hearing Aids

Description:
Designed for individuals with severe to profound hearing loss, these hearing aids offer the highest levels of amplification.
Larger in size to accommodate powerful amplifiers and larger batteries.
Suitability:
Suitable for severe to profound hearing loss.
Features:
High-powered amplification.
May include telecoil and other advanced features to enhance hearing in different environments.
Advantages:
Provides the necessary amplification for severe hearing loss.
Disadvantages:
Larger and more visible.
Can be heavier and may require a custom earmold for optimal fit.
5. BTE Hearing Aids with Earmolds
Description:
These BTE hearing aids use custom-made earmolds that fit the contours of the ear for a secure and comfortable fit.
Suitability:
Suitable for all degrees of hearing loss, especially for individuals with more severe loss.
Features:
Custom fit to ensure comfort and optimal sound delivery.
Helps reduce feedback and improve sound quality.
Advantages:
Secure and comfortable fit.
Can be used with various BTE models.
Disadvantages:
Requires custom molding, which can take time and may need adjustments.

How to Use Behind-the-Ear Hearing Aids?
Using your behind-the-ear hearing aid is simple:
- Place the hearing aid behind your ear, ensuring a snug fit.
- Insert the earpiece or receiver into your ear canal.
- Adjust the volume and settings as needed using the controls on the hearing aid.
How to Clean Behind-the-Ear Hearing Aids?
Proper maintenance is key to keeping your behind the-ear hearing aid in top condition:
- Wipe the hearing aid with a soft, dry cloth to remove any dirt or debris.
- Use a brush or pick to clean the microphone and receiver ports.
- Avoid exposing the hearing aid to moisture or liquids.
- Store the hearing aid in a dry, cool place when not in use.
- Use a soft, dry cloth to wipe the exterior of the hearing aid daily.
- Use a hearing aid brush to remove wax and debris from the microphone and receiver ports.
- Do not use water or cleaning agents because they may harm the device.
- When not in use, keep the hearing aid somewhere dry and cool.
Considerations When Choosing BTE Hearing Aids
When choosing Behind-the-Ear (BTE) hearing aids, there are several important considerations to ensure you select the right device for your specific needs and lifestyle. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you make an informed decision:
Degree of Hearing Loss
- Mild to Moderate Loss: Mini BTE or RITE/RIC models might be suitable due to their discreet design and comfort.
- Severe to Profound Loss: Standard BTE or Power BTE models provide the necessary amplification and features to handle more significant hearing loss.
2.Lifestyle Needs
- Active Lifestyle: Consider moisture-resistant or waterproof models if you are frequently exposed to sweat, rain, or high humidity.
Retention clips or sports locks can help keep the hearing aids secure during physical activities. - Quiet Environments: Basic models might be sufficient if you spend most of your time in quiet settings.
- Noisy Environments: Look for BTE hearing aids with advanced noise reduction and directional microphones to improve speech understanding in noisy places.
Comfort and Fit
- Earmold Fit: Custom earmolds ensure a secure and comfortable fit, especially important for extended wear.
- Open-Fit Domes: These are more comfortable and less occlusive, suitable for those with mild to moderate hearing loss.
4. Technology and Features
- Sound Processing: Advanced digital sound processing provides clearer and more natural sound quality.
- Bluetooth Connectivity: Allows for direct streaming from smartphones, TVs, and other devices, which can be crucial for modern lifestyles.
- Rechargeable Batteries: Convenient and environmentally friendly, eliminating the need to frequently replace batteries.
- Telecoil (T-Coil): Enhances hearing in public places with hearing loop systems, such as theaters and churches.
- Directional Microphones: Improves ability to focus on specific sounds, particularly in noisy environments.
- Feedback Cancellation: Prevents whistling sounds, enhancing listening comfort.
5. Ease of Use
- Manual Controls: Some models have physical buttons for volume and program changes, which can be easier to use for those with dexterity issues.
- Remote Controls: Allow for discreet and easy adjustments.
- Smartphone Apps: Many modern hearing aids come with apps that offer extensive customization and control features.
- 6. Aesthetics
- Discreet Design: Mini BTE or RITE/RIC models are more discreet and often preferred by users who are conscious of visibility.
- Color Options: Some hearing aids come in different colors to match hair or skin tone for a more personalized look.
7. Budget
- Cost: Hearing aids range in price based on features and technology levels. Determine your budget and find the best features available within that range.
- Insurance and Financing: Check if your insurance covers hearing aids or if there are financing options available.
8. Aftercare and Support
- Warranty: Look for hearing aids with comprehensive warranties covering repairs and replacements.
- Audiologist Support: Ensure that your provider offers ongoing support for fitting adjustments, maintenance, and troubleshooting.
9. Trial Period and Return Policy
- Trial Period: Many providers offer a trial period during which you can test the hearing aids in your daily life to ensure they meet your needs.
- Return Policy: Understand the terms for returning or exchanging hearing aids if they do not meet your expectations.
10. User Reviews and Recommendations
- Testimonials: Reading reviews and testimonials from other users can provide insights into the real-world performance and reliability of the hearing aids.
- Professional Recommendations: An audiologist can offer personalized recommendations based on your hearing test results and lifestyle needs.
Types
- Completely-in-Canal (CIC)
- Invisible-in-Canal (IIC)
- In-the-canal (ITC)
- Receiver-in-Canal (RIC)
- Receiver-in-Ear (RIE)
Accessories and Tools






